Contents

The Ultimate Legal Guide to Scraping Amazon Without Getting Sued or Banned
In late June 2024, Amazon launched an investigation into Perplexity AI for scraping web data against site owners’ wishes. The details are still unclear, but one thing is evident—Big Tech is cracking down on unauthorized data collection.
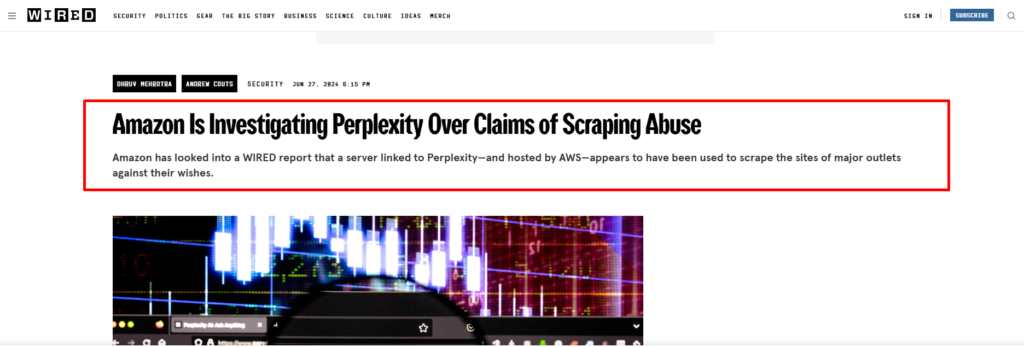
So, what does this mean for web scrapers? If a company as big as Perplexity AI is under fire, smaller players are even more vulnerable. Web scraping, when done wrong, can expose your IP address, result in lawsuits or fines, and, in extreme cases, even lead to criminal charges.
As if that weren’t enough, Amazon tightens its defenses daily and guards its data like a hawk. In short, playing it safe is getting trickier!
With so much fear-mongering and misinformation about what’s legal and what’s not, how do you know where to draw the line?
That’s precisely why we wrote this guide—to cut through the noise and bring you clarity. We’ll break down Amazon’s anti-scraping defenses, show you how to navigate them legally, and even recommend the best Amazon scrapers.
Let’s get started!
What Makes Scraping Amazon Legally Risky?
Web scraping Amazon might seem like a straightforward process. The platform’s product listings, prices, and reviews are publicly accessible, so there are no ties, right?
Hell, no!
Beneath the surface, several legal risks are waiting to prey on you. Before you know it, you’ll be facing lawsuits, hefty fines, or even criminal charges. It’s that bad.
So before you go scraping Amazon aimlessly, here are some key U.S laws you can’t ignore:
The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA)
The CFAA was legalized in 1986 and is the U.S.’s primary anti-hacking law.
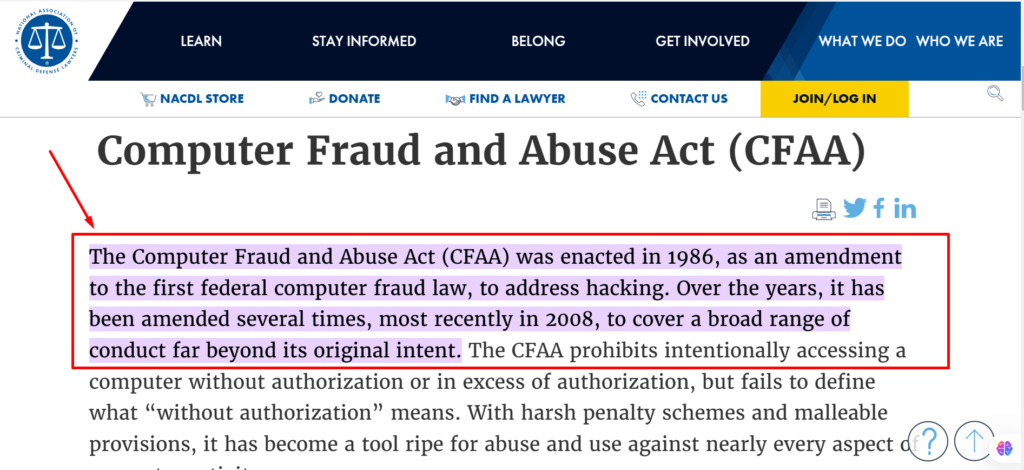
When it was approved, it was mainly used to fight cybercrime. Today, courts have interpreted it and applied it to web scraping in cases where access to a website is considered “unauthorized.”
Under the CFAA, scraping Amazon could be illegal if you bypass its technical barriers, such as login pages and IP blocks. The law can also apply when you violate Amazon’s Terms of Service (ToS), which clearly prohibits automated data extraction:

A great shift for this act was the 2021 Supreme Court case of Van Buren vs. United States, in which the court narrowed its scope.
It stated that accessing publicly available information without authorization does not violate the CFAA. However, evading technical restrictions does.
Now, what does this mean for Amazon Scrapers?
The scrapers should allow you to scrape public product pages without hacking into accounts or bypassing technical walls set by Amazon.
This act has a bit of back-and-forth because we’ve seen companies aggressively pursue scrapers and companies under the CFAA, such as in the HiQ, LinkedIn, and Craiglist vs. 3taps cases.

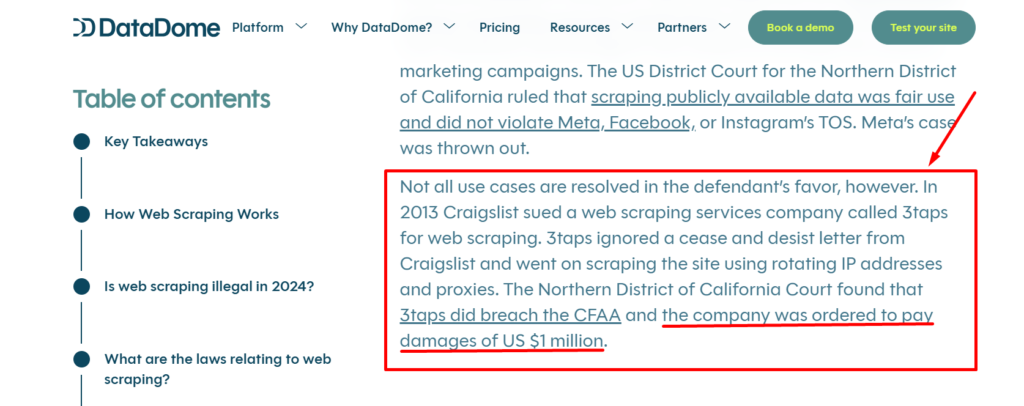
Our advice:
Respect Amazon’s laws. Avoid bypassing the technical barriers or trying to hack into accounts.
Most importantly, avoid advice that convinces you otherwise; here’s an example:
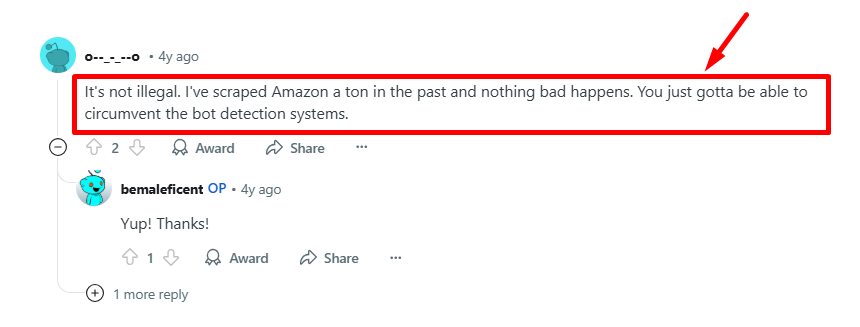
Remember, trying to avoid necessary detections makes your scraping activity seem suspicious.
The Copyright Law
Amazon’s product descriptions, images, and branded content are all protected under U.S. copyright law.

While factual data such as prices and product specs aren’t copyrightable, creative elements are 1000% in the copyright category. The creative elements include;
- Marketing Copy
- Photography
- User Reviews (If original)
Go here for the entire list of copyright and trademarked elements, which Amazon indicates is non-exhaustive (meaning there’s more).
If you scrape and republish elements like your own without permission, you could be accused of infringement, and things could get a bit ugly.
Let’s take a quick example. You decide to scrape Amazon and have everything ready, even a scraper that you didn’t do a deep dive into. You use the tool, and it copies the images displayed on your competitor’s site.
When you use those images anywhere online, Amazon can sue you for copyright violations.
It doesn’t stop there. If the scraper also copies reviews and you use them without changing or anonymizing them, you can be sued for infringing on the original author’s rights.
So what should you do?
Our advice:
Choose an Amazon scraper that can distinguish between unprotected facts, such as a product’s dimensions, and protected creative works, such as a detailed customer review or analysis.
We’ve talked about choosing the right Amazon scrapers before, so if you want more info on that, check out:
And guess what? Amazon’s eyes are not the only ones spying on you while you collect all the copyright data you shouldn’t be collecting.
And guess what? Amazon’s eyes are not the only ones spying on you while you collect all the copyright data you shouldn’t be collecting.

The Digital Millenium Copyright Act (DMCA)
Now, if you thought the rules were too much, we’re just getting started. The DMCA adds another risk layer to Amazon scraping.
Section 1201 of this act prohibits bypassing technological measures that control access to copyrighted materials.
Do you remember when we talked about trying to bypass detections? Here’s where you can easily be sued!
Amazon already has several security barriers, including CAPTCHAs and IP rate limits (which we all hate!).
When you try to scrape any form of data, whether copyrighted or not, by bypassing Amazon’s protocols, you qualify as a candidate for legal action.
One of the most common ways most individuals fall into this deadly trap is by using headless browsers and proxy networks to escape Amazon’s bot detection system.
It’s unfortunate because if you think about it, it’s just escaping a cold cup of coffee and going directly for soup from a cooking pot. Tell us, which is hotter?
Our Advice:
Go for a compliant scraper! You can never be too safe, as Amazon is always going the extra mile to protect its data and that of its consumers.
Also, DMCA is not just about what you scrape but how you scrape, so think about that!
Data Privacy Laws
Now, enough of the copyright laws, let’s look at data privacy regulations.
Even seemingly harmless data, such as product reviews, can contain personal information that can immediately trigger compliance issues.
To set things straight, two main data privacy laws have significant effects on Amazon:
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and,
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR applies mainly to scraping data that is tied to EU residents. This includes:
- Reviews with usernames
- Locations
- Other Identifiers
Under GDPR, personal data should only be collected with consent from a legitimate legal basis. This is something most Amazon scrapers lack!
For example, when scraping Amazon.de (Germany) reviews that include a user’s first name and city, the following GDPR compliance should be included:
- Providing transparency about data collection.
- Allowing users to request the deletion of their data.
- Implementing “privacy by design” in your scraping workflow.
While this may seem like a simple procedure, violating this law comes with harsh fines. You can be charged up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue—whichever is higher.

One of the most prominent cases seen as a result of violating GDPR was between Kaspr and Linkedin.
The French Data Protection Authority, CNIL, fined Kaspr for violating GDPR rules related to data scraping on LinkedIn.
The company was fined €240,000 for collecting and storing LinkedIn users’ contact details without proper authorization. Its practices included scraping data from users with restricted visibility of their first—and second-degree connections.
The CNIL ordered Kaspr to cease unlawful practices, delete improperly collected data, and improve transparency and compliance with GDPR requirements.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA gives residents the right to know what personal data is collected about them and allows them to opt out of the sale of their data.

So, how does this affect you while scraping?
If your scraping tool collects data on California-based Amazon users, such as the profile linked to their emails, you might easily fall into CCPA’s trap.
You are left with two options. Either comply with CCPA requirements or face penalties of up to $7,500 per intentional violation.

If you want to escape all these tantrums, use our Amazon scrapers.
Why?
The only thing you’ll ever have to do is copy and paste the link on the scrapers.
You’ll never:
- Be caught using a headless browser
- Chase Amazon for scraping permission
- Struggle to collect publicly available Amazon Data
- Find yourself tangled in infringement claims and have legal cases
- Second-guess whether the data you are scraping is copyrighted or not
Here are the hand-picked scrapers we have for you:

We have a special bonus for you to try out any of these scrapers;
For step-by-step guidance on how each of these scrapers works, check out these guides;
Amazon's Anti-Scraping Defenses and How to Navigate Them
Amazon has one of those ‘sophisticated’ and complex anti-scraping measures, which means your scraping conduct and activities should also be high-level.
Here’s a breakdown of the key characteristics of Amazon’s anti-scraping procedures and how you can go about them:
| Amazon's Defense Mechanism | Key Characteristics | Navigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Behavioral Fingerprinting | • Amazon tracks mouse movement, scroll speed, typing patterns, and over time. • It also flags precise, repetitive, or linear navigation as bot-like behavior. • It also detects "too-perfect" browsing actions that don't resemble human interactions. | • Randomize your scroll speeds and introduce idle times between your actions. • Use human-like cursor movements and have unpredictable pauses. • Vary your click intervals and introduce scrolling changes. |
| Device & Network Fingerprinting | • Amazon identifies patterns in headers, user agents, and connection types. • It also tracks timezone inconsistencies and in-screen resolutions. | • Use anti-fingerprinting browser tools like our scrapers. • Ensure user-agent strings match your actual browser and OS data. |
| Real-Time Adaptive Risk Scoring | • Amazon adjusts security measures dynamically based on volume and anomalies. • It can also temporarily shadow-ban suspected bot traffic instead of having instant blocking. | • Monitor your response codes and adjust requests in real time. • Deploy self-learning throttling to stay below detection thresholds. • Avoid request bursts by distributing your scraping across different time slots. |
| Evolving CAPTCHA Challenges | • Amazon uses reCAPTCHA v3, hCaptcha, and invisible challenges. • It also adjusts difficulty based on detected risk. • Plus, Amazon detects high-risk sessions and forces more frequent CAPTCHA verifications. | • Avoid actions that trigger CAPTCHAs (e.g., rapid refreshes, aggressive data extraction). • Use real browser sessions to reduce CAPTCHA occurrences. • Manually solve CAPTCHAs where necessary (rather than bypassing them entirely). Don't be lazy! |
| Rate Limiting & IP Blocking | • Amazon limits requests per IP and flags excessive traffic. • The platform can also differentiate between residential and data center proxies. • It also detects multiple failed connection attempts as suspicious activity. | • Use high-quality rotating residential proxies with user-like browsing. • Maintain a natural request frequency to avoid spikes. • Alternate between different entry points, such as the search and direct product pages. |
| JavaScript Challenges & Honeypots | • Amazon uses hidden JS checks that bots fail (e.g., cookie verification, DOM changes). • It also distributes deceptive UI elements to catch automation scripts. | • Use real browsers instead of pure HTTP requests. • Parse and execute JavaScript to pass hidden tests. • Monitor page elements for unexpected changes that could indicate a bot trap. |
| Data Integrity & Anomaly Detection | • Amazon compares historical behavior to detect sudden traffic spikes. • Machine learning is used to identify scrapers mimicking normal users. • It also detects inconsistencies between session length, interaction depth, and request pattern. | • Spread your requests over different time zones. • Rotate session fingerprints instead of reusing the same identity. • Monitor success/failure ratios and tweak your approaches accordingly. |
Summing It Up
“Ignorance is bliss” — but not when scraping Amazon.
Scraping Amazon legally isn’t just about avoiding lawsuits; it’s about knowing where the lines are drawn and ensuring you don’t cross them.
Every move matters, from CFAA and copyright laws to GDPR and Amazon’s anti-scraping defenses.
So, what’s the best approach? It’s actually really simple: use publicly available data, stop trying to play cat-and-mouse with Amazon’s security measures, and use tools that comply with legal and ethical guidelines.
For all these benefits and so much more, give ScrapeLead a shot! Unlike shady scrapers that get blocked within minutes, it’s designed to extract Amazon data legally and efficiently without triggering bans or violating policies.
Don’t gamble with your scraping strategy. Use the right tools, follow the rules, and collect the data without the drama.
FAQs
Yes, but you must still follow Amazon’s rules and global laws like GDPR and CFAA. Amazon can block or take legal action against you, no matter where you are.
Public data like titles and prices are generally safer, but Amazon’s Terms of Service prohibit scraping without permission.
Scraping reviews with personal data (like names or profiles) violates GDPR. To stay compliant, use anonymized review data.
Use a trusted company like ScrapeLead. It offers Amazon scrapers designed to extract data legally and avoid bans.
Start scraping instantly
Sign up now, and get free 500 credits everymonth.
No credit card required!
Related Blog

Comparing The Top 5 AI Web Scraping Tools of 2025
Discover the best AI web scraper for your data extraction needs as we break down their features, pros, cons, and pricing details.

How to Scrape Apartments.com: A No-Code Guide
Learn how to use an apartments.com scraper to extract rental data, track market trends, and gain real estate insights.

4 Best Social Media Scrapers for 2025
Explore the best social media crawlers for Instagram, Facebook, YouTube & Twitter. Extract data easily with ScrapeLead’s powerful tools.

